Basel Committee Releases Updated Report on 2023 Banking Turmoil
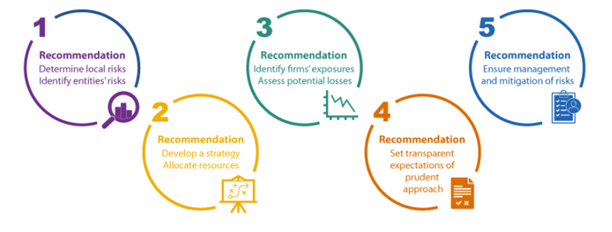
2024-10-25The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision issued a progress report to the G20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors regarding their analysis of the 2023 banking turmoil. It addresses the liquidity-related issues including distressed banks’ outflow rates and the role of the supervisory monitoring tools.
The report notes that liquidity supervision may need to evolve over time based on challenges highlighted by the 2023 banking turmoil. The challenges were related to the speed and volume of deposit outflows and changes in the banks’ funding profile, the importance of banks operational readiness to access central bank liquidity facilities, proper liquidity stress testing, and the role of social media and the digitalization of financing in hastening the speed of a banks’ distress.
Click here to read the full report.